A key focus for I-TECH in Ukraine is strengthening the capacity of local partners to develop and deliver high-quality clinical trainings and expand the supply of skilled health care workers.
Category: Clinical Mentoring
Scott Barnhart

Scott Barnhart, MD, MPH, has an extensive background as Professor of Global Health and former Director of Global Health Programs for I-TECH at the University of Washington. He has had responsibility for leading nine country offices, projects in 14 countries, and more than 500 staff. This experience and training has included extensive clinical work, research and program management in pulmonary and environmental and occupational medicine, and more than eight years as Medical Director of a safety net/Level 1 Trauma Center hospital.
Ensuring health systems can quickly detect and respond to emerging health threats is a critical challenge in both domestic and global health. Dr. Barnhart’s major implementation projects include scale-up of voluntary medical male circumcision (VMMC) in Zimbabwe and Malawi, OpenMRS, and laboratory information systems. Dr. Barnhart deploys his expertise in multiple African countries and Haiti to strengthen health systems and health care.
A goal of Dr. Barnhart’s work is to promote country-led, country owned sustainable development. Consistent with the principles of the Paris Declaration, the goal is to transition the bulk of development work and the associated leadership, ownership, technical direction and control of funding into the countries where development occurs. This approach ensures that the entire continuum of skills necessary for development (technical expertise, administration (human resources, operations, and management and accountability for funds) is transitioned to local partners. A key indicator is to have 75% or more of a grant’s funding expended in-country on local programs and local citizens and to support the local economies in these highly resourced constrained countries. Dr. Barnhart has worked closely to advance this model through projects in Haiti with a goal to shift the majority of a project to a local organization and in Zimbabwe where the VMMC program is largely run through local partners.
Program Highlights
Clinical Mentoring in Haiti
I-TECH introduced its clinical mentoring program in Haiti in 2006. A team of physicians, nurses, and psychologists provide technical assistance to 20 sites in the MSPP care and services network to help strengthen HIV- and AIDS-related services. During site visits, CHARESS mentors conduct clinical rounds Continue reading “Clinical Mentoring in Haiti”
Patient-Trainers are Key to Providing High-Quality Care to MSM, Sex Worker, and Transgender Communities in the Caribbean

For many communities in the Caribbean Region, barriers to high-quality HIV treatment and care often arise before a client crosses the clinician’s threshold.
“When [key populations] access health care – and when we say key populations, we mean MSM [men who have sex with men], sex workers, transgender people – they are immediately discriminated against,” says Kenyatta Barnaby, a Key Populations (KP) Advisor working with the International Training and Education Center for Health (I-TECH) in Jamaica.
“They can’t relate to the clinician or anyone in their surroundings,” continues Barnaby, “and before they even get to [see] the clinician, there is discrimination in the waiting area.”
If a patient makes it far enough to see a clinician, the stakes become higher – misunderstandings and miscommunication can have grave consequences. Barnaby notes that, often, clients from key populations are afraid to contradict a clinician’s assumptions and may not share information that’s vital to receiving proper care.
When clients do disclose that they are gay, transgender, or doing sex work, “[a clinician] might express disgust or alarm,” explains Conrad Mitchell, I-TECH’s Key Populations Advisor in Trinidad & Tobago. “What happens directly as a result of that is that someone feels alienated, and therefore does not come back and does not get the care that they need.”
When these experiences are shared within community networks, it can result in fewer people from key population groups accessing care at facilities where others have had negative experiences.
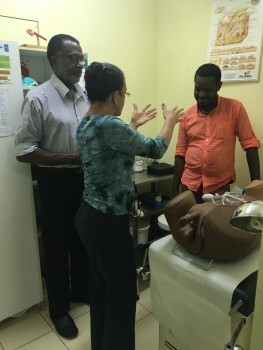
A novel approach using real-world experiences
To address these challenges in HIV care and treatment settings, I-TECH designed and launched Improving HIV Care for Key Populations in the Caribbean, a novel preceptorship program aimed at building clinicians’ capacity to provide nonjudgmental, high-quality, comprehensive HIV care to most-at-risk communities.
The two-day intensive training occurs in a simulated clinic setting, using targeted role-play scenarios based on real-world experiences. “Patients” are portrayed by skilled KP patient-trainers under the supervision of an experienced clinical facilitator. Clinician trainees participate in 8 to 12 different clinical scenarios featuring patients who are transgender, MSM, or doing sex work.
During these trainings, clinicians practice taking a comprehensive sexual history, performing a proper (simulated) ano-genital examination with appropriate site-specific STD screening, conducting rapid mental health screenings, and undertaking individual risk assessment and risk reduction counseling.
The program was developed and implemented by I-TECH in close collaboration with key population groups in in the region. I-TECH developed standardized case scenarios collaboratively with community members, and recruited and trained representatives from the sex worker, MSM, and transgender communities in each country to portray these scenarios as the patient-trainer and to give targeted feedback to clinicians.
Frank, face-to-face discussions
Once the trainer exits the role of “patient,” the clinician is also afforded the opportunity to have a frank and open discussion with the trainer. These conversations are wide-ranging – from the obstacles that prevent key populations from accessing care; to the health care issues they face; to psychosocial issues such as mental health, gender affirmation, gender-based violence, and substance abuse.
“One of the great things that can come out of something like this,” says Mitchell, “is although the person has come in with a physical problem, we are sensitizing the clinician to see past that.”
The patient-trainers share powerful personal stories with the clinicians, noting how small actions or expressions – such as a slight grimace or donning gloves to take blood pressure – can be interpreted as stigma. They offer insight into what runs through a patient’s mind at a health facility: fear of harassment by vendors, security staff, and other patients; anxiety around disclosing they have same-sex partners, the number of partners, or sexual practices; and reluctance to seek care for ano-genital conditions.
The patient-trainers also teach providers about the importance of using preferred names and pronouns, about avoiding the assumption of heterosexuality, and of showing a non-judgmental attitude. “A lot of it is about language,” says Barnaby. “We are equipping them with the knowledge of how to speak to a KP person without discriminating.”

A two-way street
For some clinicians, this training is the first time meeting a transgender person, or the first time receiving constructive feedback about service delivery from the perspective of the patient. Clinicians have noted that they appreciate opportunities to interact with real people from the key population groups and to get feedback on their clinical practice and interpersonal skills directly from a patient’s perspective.
Mitchell, who portrays several patients throughout the training program in Trinidad, also notes that “there is always that ‘wow’ moment with the clinicians: ‘Wow, I didn’t know this was happening.’” Mitchell says that he had a clinician admit to him that the many years of schooling that doctors go through can leave them naïve of social issues.
Perhaps most valuably, the understanding is not one-sided. At the end of the two days, says Mitchell, not only is there a marked improvement in the clinicians, but the patient-trainers come away enlightened, as well.
“Often we forget that doctors are people themselves,” he says. “I think that’s one of the things that the team in Trinidad collectively learned. Because there were a number of doctors that came to the training, and we had sort of a negative view of them…. Often what comes across as negative is this person having a rough day, a bad day, or not being able to give the kind of help they want to give.”
Barnaby echoes that sentiment, noting that a doctor can quickly get a bad reputation within the tight-knit KP communities in Jamaica, and these trainings have helped bridge the gap from both sides. “If the preceptorship trainers can see the doctor’s potential to be good,” says Barnaby, “he gets a good rep in the community, as well.”
So far the program has trained 20 clinicians from the highest volume HIV care and treatment clinics in Jamaica and Trinidad. In the coming year, I-TECH will continue to train clinicians and will also adapt the training for nurses in the region.
THIS PROJECT IS SUPPORTED BY THE HEALTH RESOURCES AND SERVICES ADMINISTRATION (HRSA) OF THE U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES (HHS) UNDER U91HA06801, THE INTERNATIONAL AIDS EDUCATION AND TRAINING CENTER (IAETC). THE CONTENT OF THIS POST IS THE AUTHOR’S AND SHOULD NOT BE CONSTRUED AS THE OFFICIAL POSITION OR POLICY OF, NOR SHOULD ANY ENDORSEMENTS BE INFERRED BY HRSA, HHS OR THE U.S. GOVERNMENT.
Launch of HIV Programs in Zimbabwe Hits the Right Note
To the brass beats of the Prince Edward School Jazz Band, on Feb. 6, a crowd of approximately 150 government officials, health professionals, and members of the press celebrated the launch of three programs in Zimbabwe, two of which are implemented by I-TECH Zimbabwe and partners. These vital programs aim to build local capacity and provide comprehensive services to prevent and combat HIV/AIDS in the country.
Speaking at the festivities were David Bruce Wharton, U.S. Ambassador to the Republic of Zimbabwe; Dr. Owen Mugurungi, director of the AIDS and TB Unit at the Ministry of Health and Child Care (MOHCC); Dr. King Holmes, Chair of the Department of Global Health at the University of Washington; Dr. Ann Downer, Executive Director of the International Training and Education Center for Health (I-TECH); and Dr. Batsirai Makunike-Chikwinya, Country Director of I-TECH Zimbabwe.
“Preventing the spread of HIV/AIDS is important to all of us, as is providing the best level of care to those living with this disease,” said Amb. Wharton. “Today we celebrate the launch of programs that will help us reach these goals together – programs that were designed together, by dedicated teams of collaborating partners from Zimbabwe and from the United States.”
In this spirit of collaboration, the programs, totaling $65 million over five years, support the Zimbabwe MOHCC with grant funding by the U.S. President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR), technical support from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and implementation by local and U.S.-based partners. These partners include I-TECH; Zimbabwe Association of Church-Related Hospitals; Zimbabwe Community Health Intervention Research Project; Compre Health Services; The Newlands Clinic and Newlands Clinic Training Centre; Pangaea Global AIDS Foundation, Zimbabwe; and the University of Zimbabwe-University of California, San Francisco Collaborative Research Programme.
The Training and Mentoring Program seeks to develop and deliver in-service training on antiretroviral therapy, including the medical management of HIV/AIDS, women’s reproductive health, tuberculosis (TB), and TB/HIV co-infection to 8,000 health care workers across the country over five years. A mentorship component will also provide health care workers with access to ongoing learning and feedback on clinical issues. Health workers will receive refresher trainings via distance learning technologies, and the effectiveness of the program will be measured through a training database.
Also celebrated – and accompanied by a ribbon-cutting and presentation of 17 new vehicles – was the launch of the Voluntary Medical Male Circumcision Program. The program, building on work that started last spring, seeks to deliver services to 412,000 men in Zimbabwe between the ages of 15 and 49 years over the next five years. Medical male circumcision has proved very effective in preventing the spread of HIV. Randomized controlled trials in Uganda, Kenya, and South Africa have shown that this intervention reduces the risk of female-to-male sexual transmission of HIV by approximately 60%.
“Together, these two programs will improve the effectiveness and quality of prevention, treatment, and care services for those affected by HIV/AIDS – and create better health systems for all Zimbabweans,” said Dr. Holmes.
I-TECH Selecting Participants for New Certificate Program in Laboratory Leadership
I-TECH is currently selecting participants for a new, innovative program designed to strengthen the leadership and management skills of clinical and public health laboratory supervisors.
Photo of the Week: Clinical Mentors
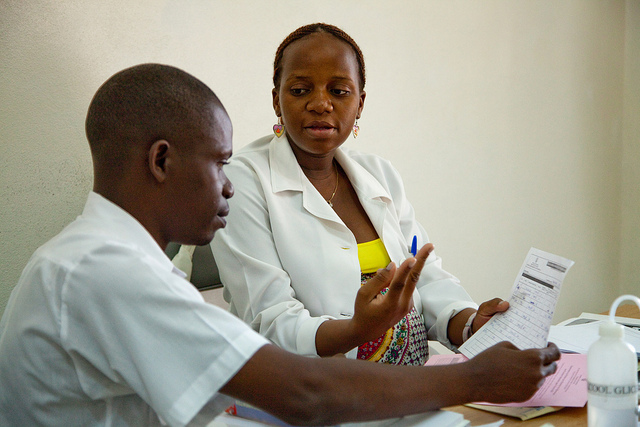

I-TECH clinical mentors work to strengthen the provision of care for people living with HIV and AIDS, tuberculosis (TB), and sexually transmitted infections (STI) by assessing and making recommendations for improvements to service-delivery systems.
