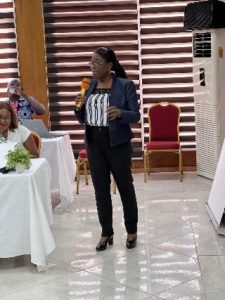It was a busy fall season for teams throughout the I-TECH Network, several of which had robust representation at end-of-year conferences including the International Conference on AIDS and STIs in Africa (ICASA) 2023 the Global Digital Health Forum (GDHF) 2023.
Welcome additions to I-TECH’s regular lineup of conferences were Infectious Disease Week (ID Week) 2023 and the 40th Annual Oregon Rural Health Conference, attended by representatives of I-TECH’s new network partner, the UW Center for Stewardship in Medicine (CSiM).
Representatives from the network presented more than a dozen posters, spoke at panels and discussions, and led an interactive workshop. Read below for more details (links to presentations will be posted as they are made available).
ICASA 2023, 4-9 December, Harare, Zimbabwe
The theme of this year’s conference was “AIDS is not over: Address inequalities, accelerate inclusion and innovation.” I-TECH Network partner the Zimbabwe Technical Assistance, Training, and Education Center for Health (Zim-TTECH) and its partners Pangaea Zimbabwe AIDS Trust (PZAT) and Zvandiri presented several posters representing their work to innovate and improve access at the training and community levels.
Zim-TTECH:
-
Gloria Gonese at ICASA 2023 Romana R Katekwe, Edson Chidovi, Frances Petracca, Batsirai Makunike, Gloria Gonese, Kerry Thomson, Zwashe Bangani, Haddi Cham, Mirriam Mugwise, Emmanuel Govha, Stefan Wiktor, “Improving Access to Quality Improvement Training through Off-line Electronic Learning: A Case Study from Zimbabwe”
- Langalokusa Sibanda, Peace Ntini, Richard Mashapa, Gloria Gonese, Rickie Malaba, Tendayi Mharadze, Ralph Makuyana, Methembe Ndlovu, Ruth Levine, Vivian Bertman, Abigail K. Korn, Kerry A. Thomson, Owen Mugurungi, Tsitsi Apollo, Getrude Ncube, Mirriam Mutseta, Beauty Nyamwanza, Batsirai Makunike-Chikwinya, Stefan Wiktor, “DREAMS Ambassadors Increase HIV Self-Testing Uptake by Male Partners of Young Women in Zimbabwe”
- Anjali Vasavada, Phibion Manyanga, Sandra Murwira, Lucia Gondongwe, Ponesai Nyika, Batsirai Makunike-Chikwinya, Gloria Gonese, Stefan Wiktor, George Mamire, Kerry A. Thomson, “Acceptance of Free Cervical Cancer Screening Among Zimbabwean WLHIV: Implications for Integration of HPV Testing into Routine HIV Care”
- Rumbidzai Dhliwayo, Lennox Dziva, Ponesai Nyika, Chiedza Mupanguri, Gloria Gonese, Tsitsi Apollo, Owen Mugurungi, Talent Maphosa, Haddi Jatou Cham, Batsirai Makunike-Chikwinya, Stefan Wiktor, “Assessing Implementation and Outcomes of Screening for Advanced HIV Disease (AHD) Among Persons Living with HIV in Five Provinces of Zimbabwe”
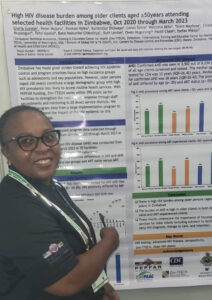
- Gloria Gonese, “High HIV disease burden among older clients aged ≥50years attending selected health facilities in Zimbabwe, Oct 2020 through March 2023”
PZAT:
- Precious Moyo, Joseph Murungu, Shamiso Nyakuwa, Casper Hera, Imelda Mahaka, Blessing Mushangwe, Phibion Manyanga, Gloria Gonese, Batsirai Makunike, Takunda Sola, Getrude Ncube, Tendayi Mharadze, Rickie Malaba, Stefan Wiktor, “Key Populations Outreach Activities for Scaling Up HIV Prevention Care and Treatment Services in Harare, Zimbabwe”
- Precious Moyo, Joseph Murungu, Shamiso Nyakuwa, Casper Hera, Imelda Mahaka, Blessing Mushangwe, Phibion Manyanga, Gloria Gonese, Batsirai Makunike, Takunda Sola, Getrude Ncube, Tendayi Mharadze, Rickie Malaba, Stefan Wiktor, “Layering Enhanced Economic Strengthening Interventions to Reduce Vulnerabilities Among Sexually Exploited Minors and Young Women Selling Sex in Zimbabwe”
- Sitshengisiwe Ruzibe, Casper Hera, Precious Moyo, Joseph Murungu, Shamiso Nyakuwa, Imelda Mahaka, Langalokusa Sibanda, Peace Ntini, Gloria Gonese, Batsirai Makunike, Mirriam Mutseta, Getrude Ncube, Tendayi Mharadze, Rickie Malaba, Kerry A. Thomson, Stefan Wiktor, “Services for Sexually Exploited Minors and Young Women Selling Sex Enrolled in DREAMS program, Matabeleland North, Zimbabwe”
Zvandiri:
- Vivian Chitiyo, Tanyaradzwa Napei, Billiart Tapesana, Ann Selberg, Edson Chidovi, Gloria Gonese, Kerry Thomson, Talent Maphosa, Haddi Cham, Ngwarai Sithole, Tsitsi Mutasa-Apollo, Nicola Willis, Stefan Wiktor, “Minimizing Interruption in Treatment (IIT) through Peer Connections of Adolescents and Young People Living with HIV in Zimbabwe”
GDHF 2023, 4-6 December, Washington, D.C.
The Digital Initiatives Group at I-TECH (DIGI), and others from I-TECH, presented their work in a number of ways at this year’s Global Digital Health Forum. GDHF is a leading global public health industry conference for technology vendors, donors, researchers, government representatives, and implementing organizations working in low- and middle-income countries.

Posters:
- Feldacker C, Murethi M, Ndhlovu D, Bisani P, Kathumba D, Samala B, Oni F, Wagaba K, Kagereki E, Wassuna B, Tweya H, “Mobile Electronic Medical Record Systems: The Community-based ART Retention and Suppression (CARES) App Design for High-Quality, Integrated Antiretroviral Therapy in Lilongwe, Malawi”
- He Y, AbuShweimeh R, Kouabenan YR, Assoa PH, Puttkammer N, Gloyd S, Wagenaar BH, Komena P, Kamelan N, Iiams-Hauser C, Pongathie A, Kouakou A, Hoffman N, Flowers J, Abiola N, Perrone LA, “Determinants of Routine Implementation for Electronic Laboratory Information Systems in Côte d’Ivoire: a Mixed-Methods Implementation Science Study”
- He Y, Kouabenan YR, Assoa PH, Puttkammer N, Gloyd S, Hoffman N, Wagenaar BH, Komena P, Kamelan N, Iiams-Hauser C, Pongathie A, Kouakou A, Flowers J, Abiola N, Perrone LA, “Perceptions and Experiences of Data-Driven Decision-Making and Data Dashboard for HIV Viral Load Testing and Early Infant Diagnosis in Côte d’Ivoire”
- Gadabu O, Manyiyo B, Yiga H, Chigoriwa C, Chirowodza L, White C, Mankowski P, Mutesasira M, Gita C, Maxwell L, Muserere C, Flowers J, “A FHIR Training Workshop to Facilitate Interoperability Between the IMPILO EHR and the LIMS System in Zimbabwe”
- Secor, A, presented by Patric Prado, “Electronic Medical Record Data Missingness and Interruption in Antiretroviral Therapy among Adults and Children Living with HIV in Haiti: A Retrospective Longitudinal Study”
Virtual Panel:
- “Building Next-Gen Digital Health Solutions On FHIR With Open Health Stack” Presenter: Patric Prado
Individual Presentations:
- “Efficiently Leveraging Individual-level Health Data For Population-level Data For Decision Making: A Call To Action For FHIR-based Secondary Data Use” Presenter: Piotr Mankowski
- “Implementation of An Online Course By MOH For Health Workers In Kenya: Strategies And Lessons For Success” Presenter: Robert Oboko
- “Applying Critical Reflection To Reimagine Global Digital Health Interventions: Introducing The (Re)imaginator” Presenter: Beth Dunbar
- “Advancing National Health Information Systems Maturity: Lessons Learnt On Implementing The Informatics-Savvy Health Organization (ISHO) Assessment And Action Planning Framework For Health Leaders In Zambia” Presenter: Kendi Mburu
- “Online Learning as an Innovation And Sustainability Initiative In Digital Health In Low And Middle Income Countries” Presenter: Robert Oboko
Topic Lounge Discussions:
- “Perceptions On The Quality Of Electronic Medical Records In LMIC” Presenter: Jan Flowers
- “Bringing Into Production A Health Information Exchange Architecture In Côte D’Ivoire: Using Open Standards And Software To Enable Cross-site Patient Histories And Real Time Dashboarding. Côte D’Ivoire HIE” Presenter: Casey Iiams-hauser
Interactive Workshop:
- “Creating, Leading, And Managing Informatics-Savvy Health Organizations (ISHO): Concept, Principles, And Application”
ID Week 2023, 11-15 October, Boston, Massachusetts
IDWeek is the joint annual meeting of the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA), the HIV Medicine Association (HIVMA), the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society (PIDS), and the Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists (SIDP). This year, CSiM presented:
- “Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Underestimates True Inappropriate Prescribing for Non-Urinary Tract Infections” Presenting author: Whitney Hartlage, PharmD
40th Annual Oregon Rural Health Conference, 11-13 October, Sunriver, Oregon
For this year’s Annual Oregon Rural Health Conference, Rupali Jain, PharmD, and Natalia Martinez-Paz, CSiM Manager, shared lessons learned in Cohort 2 of their Intensive Quality Improvement Cohort (IQIC) program and how Critical Access Hospitals can approach QI in the post-COVID-19 healthcare environment.
- Session title: “Case Study: Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Quality Improvement Projects in Critical Access Hospitals”