
From L to R: Dr. King Holmes, Dr. Olga Vystoska, and Dr. Ann Downer present the signed MOU.
On June 12 and 13, representatives from Ukraine’s Bogomolets National Medical University (NMU) visited I-TECH HQ offices at Harborview Medical Center and the University of Washington (UW) Department of Family Medicine.
NMU is the leading medical school in Ukraine, with more than 150 years of history. This visit formally launched the partnership between NMU and the UW’s I-TECH, Department of Global Health, School of Nursing, School of Medicine, and Family Medicine Department. Steps toward partnership began this spring, with a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) signed by all parties.
The visit started off with a two-hour planning meeting, during which Dr. King Holmes, chair of the UW Department of Global Health (DGH), gave an introduction to the department. This was followed by presentations by Olga Vystoska, Director of the Ukrainian Family Medicine Training Center at NMU, and other UW department representatives, who explored possible areas of collaboration. The meeting wrapped up with the exchange of signed originals of the MOU.
The Ukrainian delegation particularly appreciated the opportunity to meet I-TECH’s Executive Director, Dr. Ann Downer, and staff; learn about I-TECH’s activities; and tour the UW’s Family Medicine Clinic and Harborview Madison Clinic, which provides medical care and social services for persons living with HIV/AIDS. The group was especially impressed by a tour of the UW Institute for Simulation and Interprofessional Studies (ISIS) lab at Harborview, and Dr. Vystoska expressed interest in starting a similar lab at NMU.
The delegation also had a working meeting with Dr. Chris Behrens to discuss next steps in developing an HIV in-service training curriculum for family practitioners that I-TECH plans to pilot in Kyiv in October with Dr. Behrens’s co-facilitation.
The new Project Director of I-TECH Ukraine, Anna Shapoval, was a driving force behind this collaboration and visit.
“The I-TECH Ukraine team is excited to promote the HIV response and health care reform in Ukraine,” said Ms. Shapoval, who added that she was very pleased with how the meetings went. “We look forward to growing I-TECH’s presence in country, focusing on the most urgent issues of streamlining HIV into primary health care, advancing quality assurance and quality improvement models — as continuation of its unique experience with CLASS.”
Other potential areas of collaboration include joint research activities, publications, and library exchanges; the exchange of faculty members and students for study, teaching, and research; and joint hosting of distance education broadcasts and online courses and seminars.
Julie Stein, Technical Officer for Training Development on the I-TECH Ukraine team, expressed enthusiasm as well. “This visit was incredibly fruitful,” said Ms. Stein. “The meetings and tours generated a lot of excitement from everyone about possible future collaboration.”




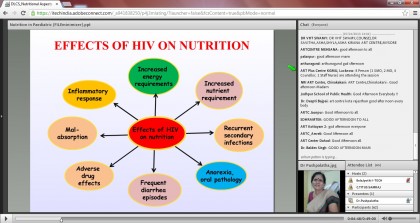 n on National ART Guidelines in 2012.
n on National ART Guidelines in 2012.